- Need Free Consultation ?

(+86) 13145896507
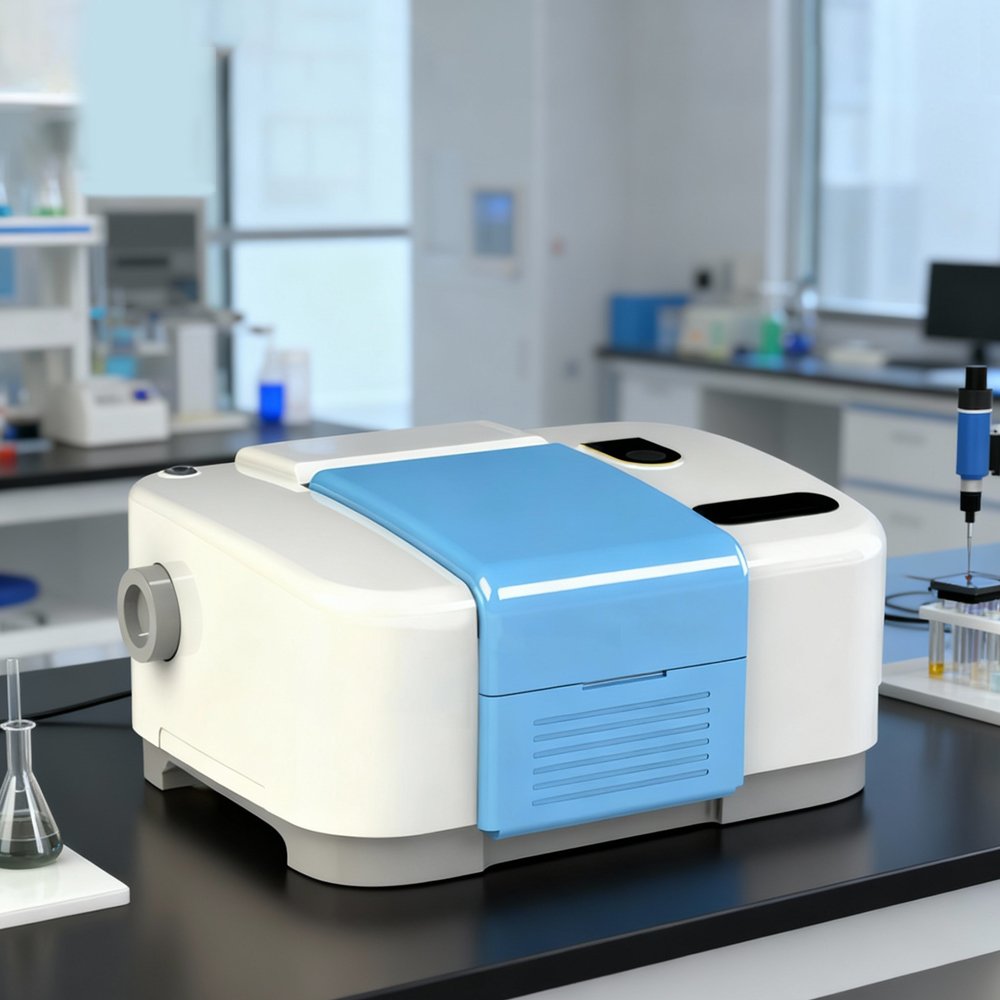
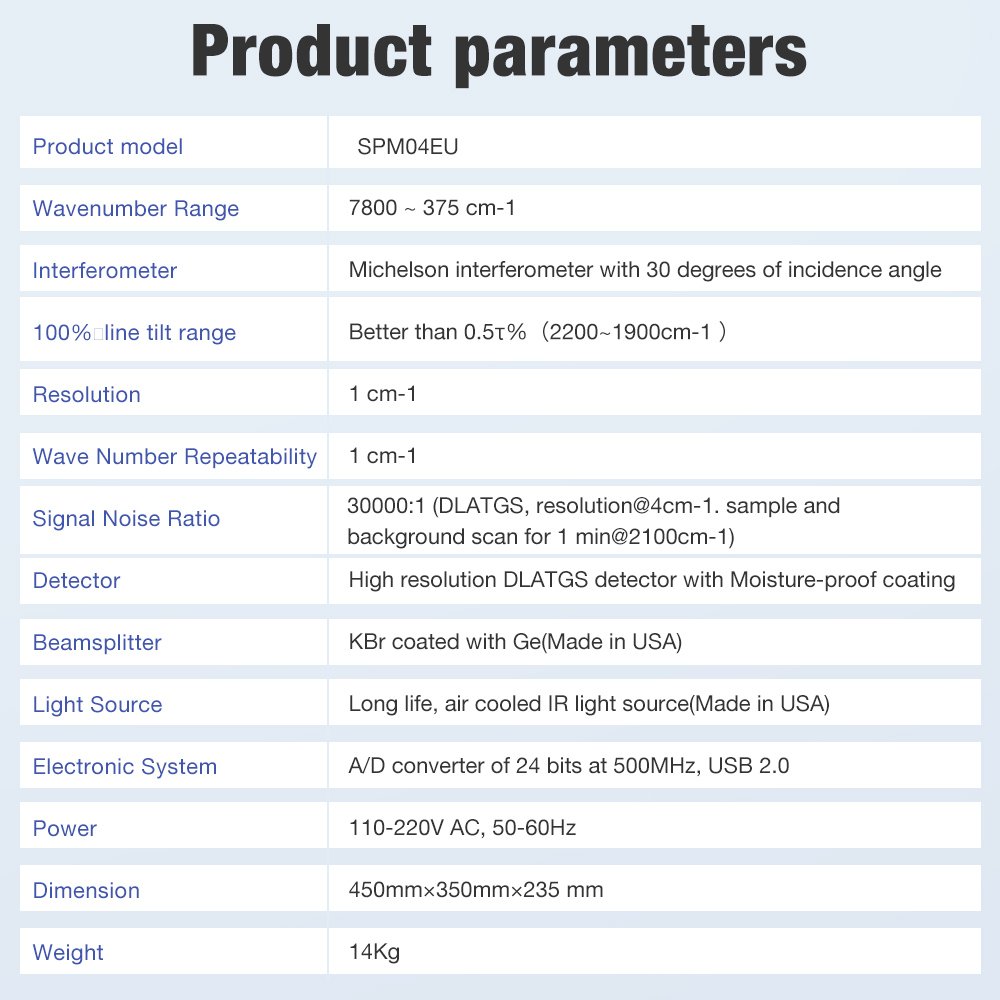
SPM04
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectrometer is a powerful analytical instrument used to identify and study the chemical composition of materials by measuring their absorption of infrared light.
Unlike traditional dispersive spectrometers, an FTIR utilizes an interferometer, typically a Michelson design with a moving mirror. This setup creates an interferogram—a complex signal of light intensity versus mirror position. The core principle is that all infrared frequencies are measured simultaneously, dramatically improving speed and sensitivity. This key advantage is known as the Fellgett or multiplex advantage.
The collected interferogram is not an immediately interpretable spectrum. It is converted into a readable infrared spectrum (intensity vs. wavenumber) through a mathematical process called the Fourier Transform, performed by a computer.
The resulting spectrum acts as a molecular “fingerprint.” Since chemical bonds vibrate at specific frequencies, they absorb infrared light at characteristic wavelengths. By analyzing the absorption peaks, scientists can identify functional groups (like C=O or O-H) and determine the molecular structure, composition, and even concentration of substances.
FTIR spectrometers are renowned for their high speed, precision, and signal-to-noise ratio. They are indispensable tools across diverse fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, environmental monitoring, and forensic analysis, for identifying organic, polymeric, and many inorganic materials.







“Excellent communication, high quality product. Timely delivery. I have been cooperating for 2 years and am satisfied with the established cooperation.”